。
# How Is Dew Point Calculated
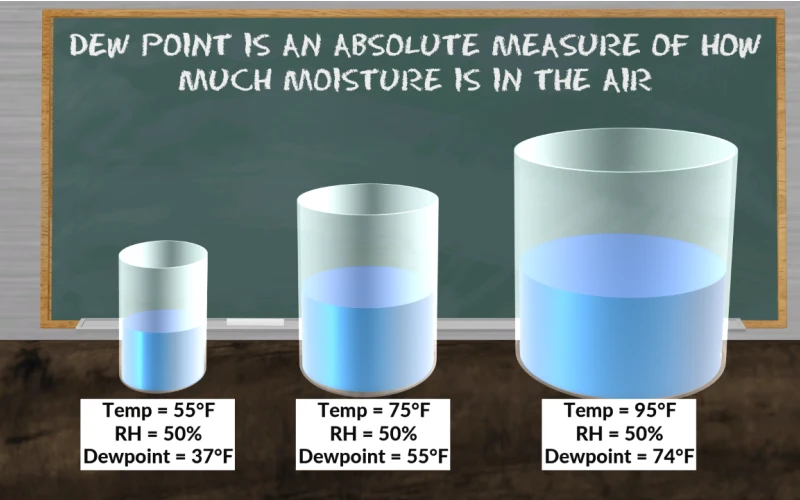
Understanding Dew Point
The dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew, fog, or frost. It is a crucial meteorological parameter that helps in understanding humidity levels and predicting weather conditions.
Basic Formula for Dew Point Calculation
The dew point can be calculated using various formulas, but one of the most common methods involves the Magnus formula. The formula is as follows:
Td = (b × α(T, RH)) / (a – α(T, RH))
Where:
- Td is the dew point temperature in °C.
- T is the air temperature in °C.
- RH is the relative humidity in percentage.
- a and b are constants (a = 17.27, b = 237.7 °C).
- α(T, RH) is a function defined as: α(T, RH) = (a × T) / (b + T) + ln(RH/100).
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the dew point, follow these steps:
- Measure the current air temperature (T) in °C and the relative humidity (RH) in percentage.
- Calculate the function α(T, RH) using the formula: α(T, RH) = (17.27 × T) / (237.7 + T) + ln(RH/100).
- Plug the value of α(T, RH) into the dew point formula: Td = (237.7 × α(T, RH)) / (17.27 – α(T, RH)).
- The result is the dew point temperature in °C.
Example Calculation
Let’s say the air temperature (T) is 25°C, and the relative humidity (RH) is 60%.
- Calculate α(T, RH): α(25, 60) = (17.27 × 25) / (237.7 + 25) + ln(60/100) ≈ 1.313 + (-0.511) ≈ 0.802.
- Calculate Td: Td = (237.7 × 0.802) / (17.27 – 0.802) ≈ 190.6 / 16.468 ≈ 11.57°C.
Thus, the dew point temperature is approximately 11.57°C.
Alternative Methods
Besides the Magnus formula, other methods like the Arden Buck equation or using psychrometric charts can also be employed to determine the dew point. Online calculators and weather instruments like hygrometers often simplify this process by providing direct readings.
Importance of Dew Point
The dew point is essential for various applications, including:
- Weather Forecasting: Helps predict fog, frost, and precipitation.
- Agriculture: Determines optimal conditions for crop growth.
- <strong
Keyword: how is dew point calculated